Pre-Fertilization: Structures and Functions
Pre-Fertilization: Structures and Functions: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Pollen Grain, Intine, Embryo Sac, Outbreeding Devices, Pollen Pistil Interaction, Vegetative Cell, Generative Cell, Dichogamy, Self Sterility, Herkogamy, Male Gametophyte, and Egg Cell.
Important Questions on Pre-Fertilization: Structures and Functions
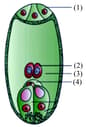
In the given figure of embryo sac, choose the option that is correctly showing the parts (1), (2), (3) and (4).
Which of the following is the device by which cross-pollination is encouraged in nature?
Match the following:
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (a) | Coleorhiza | (i) | Birth cord |
| (b) | Umbilical cord | (ii) | The outer wall of a spore or pollen grain |
| (c) | Germ pores | (iii) | A sheath protecting the root of a germinating grass or cereal grain |
Which of the following flowers undergo autogamy:
The pollen tube usually enters the embryo sac
Pollen grains are able to withstand extremes of temperature and dessication because their exine is composed of
Ploidy of ovum of angiosperms is
Find the odd one out.
Which of the following pairs has haploid structures?
Embryo sac occurs in
The male gametophyte in angiosperm is called the embryo sac.
Define male gametophyte.
Self-sterility is a common reproductive phenomenon in _____.
The term 'self-sterile' is used for describing plants which fail to set self-seed.
Pollen grains are produced by _____ of microspore mother cells that are located along the inner edge of the anther sacs.
A mature male gametophyte in angiosperms is a _____. (pollen grain/ovule)
Which is/are the haploid structure/s located in the unfertilized mature embryo sac?
Which of the following sentence/s is/are correct regarding male gametophyte?
Which of the following is/are the part/s of an embryo sac in angiosperms?
How many male gametes are formed from a pollen grain in angiosperms?
